Sources of Adult Stem Cells
The major sources of ASCs that can be obtained from a adult human are:
- Bone marrow
- Peripheral blood, and
- Adipose Tissue (Fat)
However adult stem cells have been identified in many organs and tissues, including brain, bone marrow, peripheral blood, blood vessels, adipose tissue, skeletal muscle, skin, teeth, heart, gut, liver, ovarian epithelium, and testis. They are thought to reside in a specific area of each tissue (called a “stem cell niche”).
The best source to harvest ASCs from one’s body is the adipose tissue. Below is a comparison of three sources:
- Bone marrow – About 50,000 ASCs can be harvested at any one time. These mostly become blood cells
- Peripheral blood – About 10,000 ASCs can be harvested at any one time. 50% of which will become blood cells and 50% will become tissue cells
- Adipose tissue (Fat) – About 10 to 50 million stem cells can be harvested at any one time, 5% of which will become blood cells and 95% will become tissue cells

Adipose tissue, like bone marrow, is derived from the mesenchyme and contains a supportive stroma that is easily isolated. Adipose tissue represents a source of stem cells that is having far-reaching effects in a large number of fields of medicine
Scientists at Monash Immunology and Stem Cell Laboratories (‘MISCL’) – as well as other international laboratories, have been carrying out extensive research to improve our ability to manipulate stem cells so as to be able to generate specific cell types so they can be used to treat injury or disease. In addition researchers at MISCL have been carrying out research to improve our ability to grow large quantities of adult stem cells in cell culture.
Adult Adipose Derived Stem Cells
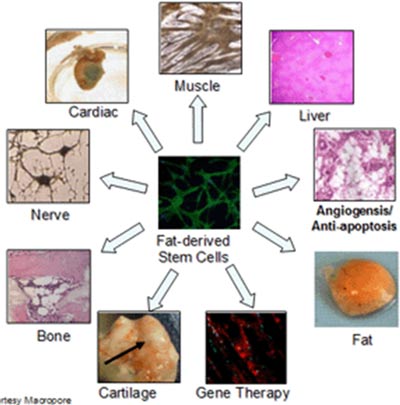
Adipose tissue represents a source of stem cells that is having far-reaching effects in a large number of fields of medicine. ADMSC cells have potential applications for the repair and regeneration of acute and chronically damaged tissues.
Adipose tissue contains a large number of stromal stem cells. Because it is easy to obtain in large quantities, adipose tissue has been found to be an ideal source of uncultured stromal stem cells. Adipose tissue, like bone marrow, is derived from the mesenchyme and contains a supportive stroma that is easily isolated. Being abundant, accessible, and replenishable, adipose tissue is an attractive source for adult stem cells that can be isolated from the adipose tissue by collagenase digestion and differential centrifugation.
Adipose-derived adult mesenchymal stem cells (ADMSC) are multipotent and can differentiate into tendon, ligament, bone, cartilage, cardiac, nerve, muscle, blood vessels, fat, and liver tissue (see figure below). The stromal fraction that is harvested from adipose tissue is a heterogeneous mixture of regenerative cells (see below).
Magellan can supply therapies based on high concentration ‘off the shelf” pure cultured stem cells or alternatively therapies based on the use of an animal’s own stromal vascular fraction (‘SVF’)
